Masouleh is the historical and tourism village and it is one of the lush with good climate and fog, in the northern of Iran . Masouleh has cool summers and snowy winters, either. Masouleh is located in the Southwestern province of Gilan in the Fooman Sardar Jangal Part, this city has 60 KM distance from the Rasht city , 36 KM distance from the Fuman city and 20 KM distance from the Maklavan city.
The old way of the Masouleh To Khalkhal that has been in the past the communication highway between Golan and Azerbaijan , in order to protect the environment, Masouleh pristine nature and spiritual heritage and preventing the degradation of natural resources, and manipulation, with the involvement of environment Protection Agency and Masouleh Cultural Heritage protected in the last decades from the Gilan.
This city in 1354 Solar Hegira have already been registered by 1090 number and put in the list of national monuments as cultural and natural heritage. Masouleh lost most of its population during the construction of new link road between the Gilan village and Azerbaijan and as well as famine in 1320.
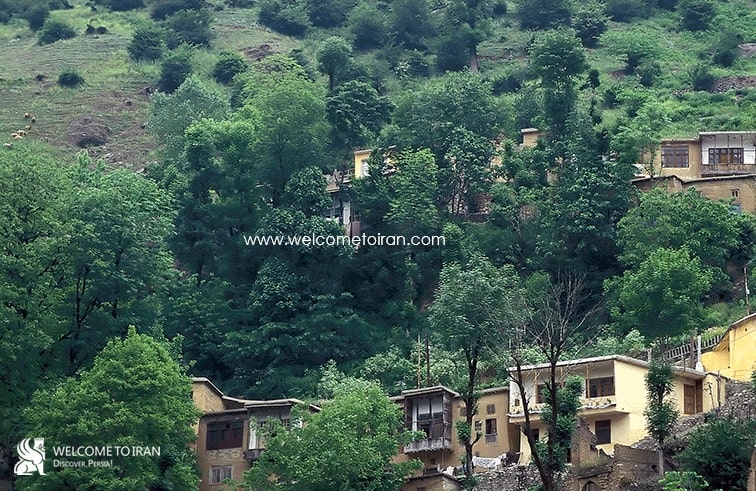

After registered the Masouleh as a cultural and natural heritage, the allow to construction and development of this village denied by the municipality (founded 1311), Cultural Heritage and Tourism Organization and the Environmental Protection Agency, and as a result, thousands of residents of this village over the past seventy years, were living in different parts of Iran, especially Tehran. Right now this city is protecting on issues such as rock falls, floods, landslides, earthquakes, capture to develop civil and human destruction. Masouleh is waiting in line for registration as a World Heritage Site to having more protections. The original language of Masouleh people is as same as the language of the people in the West of Gilan and South of Azerbaijan. Their language is Taleshi that is very close to Avesta and Tati language. The religion of them is Islam and they are Shiite.

Masouleh as a Iran tourist village
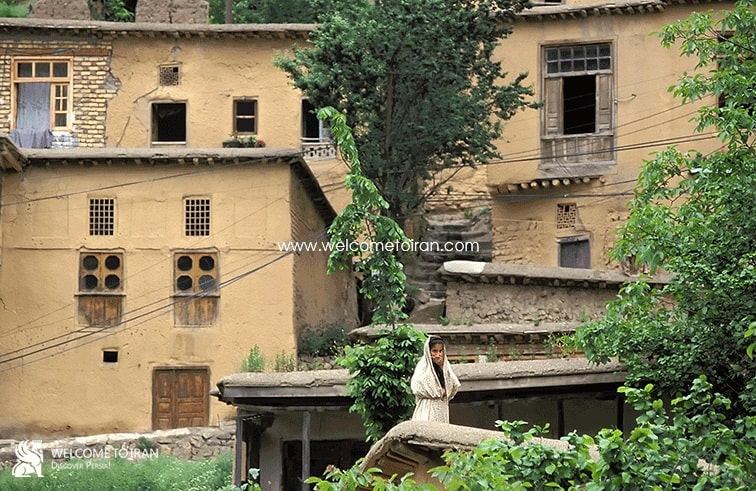
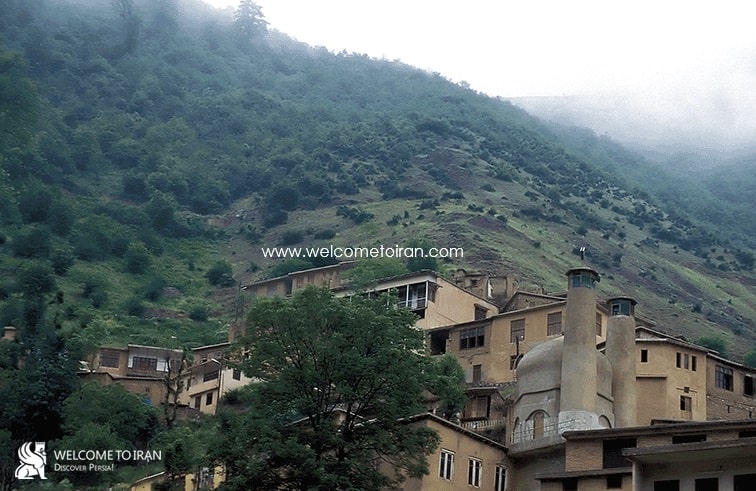
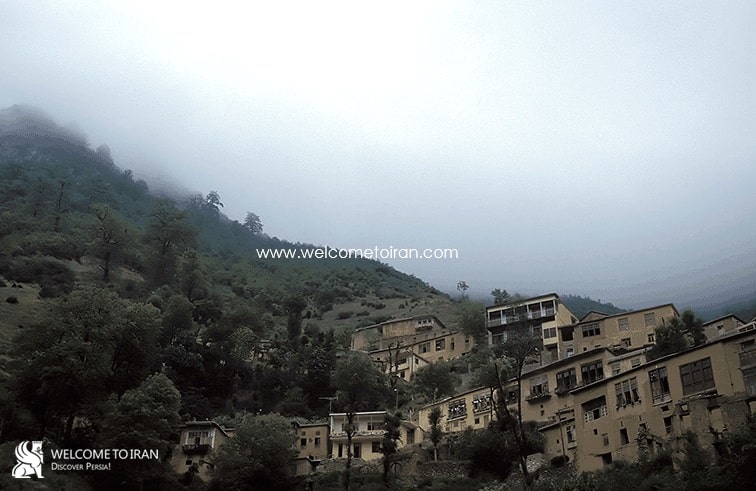
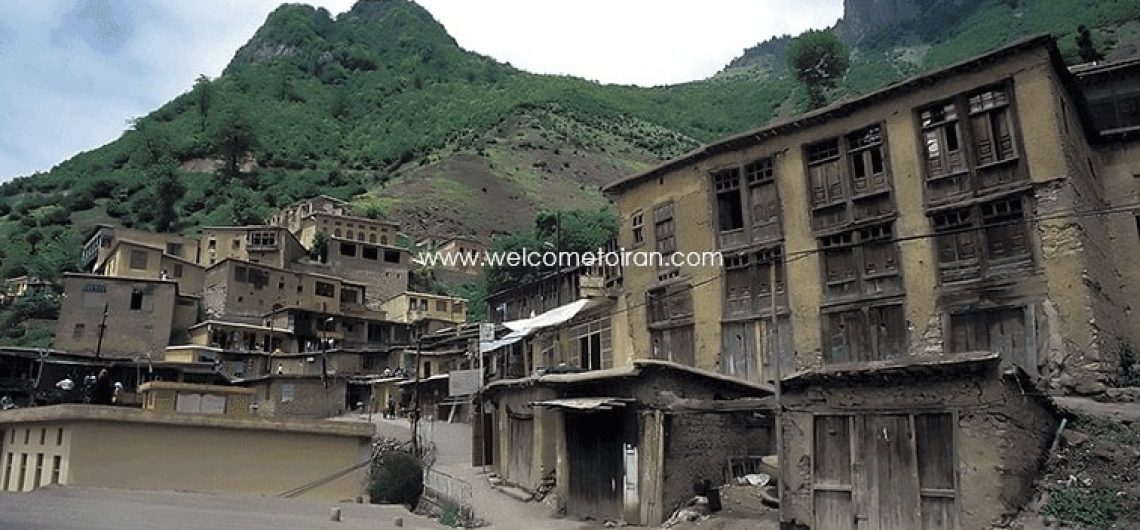
Masouleh including the extent of one hundred hectares the area under the protection of cultural heritage and natural resources is one of the best climate points of Iran that tens of thousands of tourists each year. Masouleh historical & tourism village is famous in the world due to a unique architecture. Masouleh with high mountains, forest, and Greenfield summer is one of the tourism locations in the northern regions of Iran with abundant natural visual effects especially in the late spring and summer and Shah Moalem peaks in Masouleh with 3050 meters high is the highest point of the Gilan and interesting location for mountaineering groups. Two hotels are in the traditional architecture parts of the Masouleh and several hotels are on the road that leading to the village of Iranian and foreign welcome tourists and also they are lots of hostels and rented houses in this area.
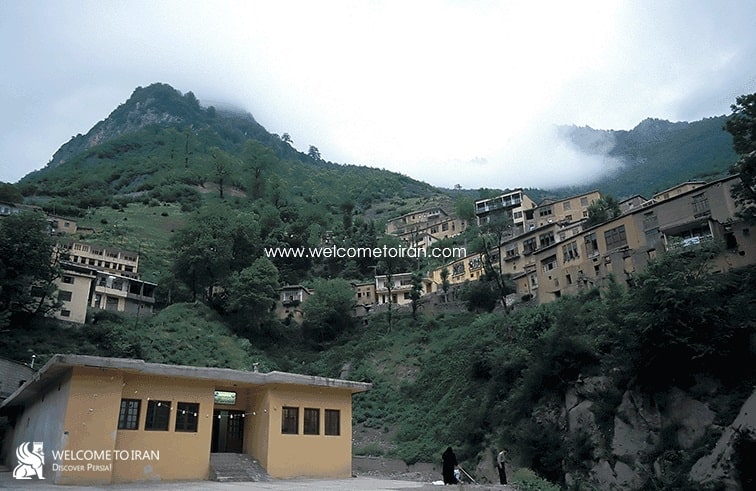

History of Masuleh Stair Stepped village
About the eighth century AD (14th century) the old people of Masouleh that is located in 6 km North West of the village with people from different parts of the vast land of Iran moved to the point that now known as Masouleh. This village lost most of its population due to the following the construction of new link road between the village of Gilan and Azerbaijan, and also the famine in 1320. Caravansaries communication highway of North and Azerbaijan were lost boom and the market traded leather and metal industries fell away. In the wake of that, most of the wealthy people of the village emigrated to the capital and other major cities and abroad. After registering the village as a cultural and natural heritage, Architectural Heritage Department and Environmental Protection Agency did not allow to construct and develop the city. Future generations settled in spotter of Iran, especially in the Northern part and Tehran.
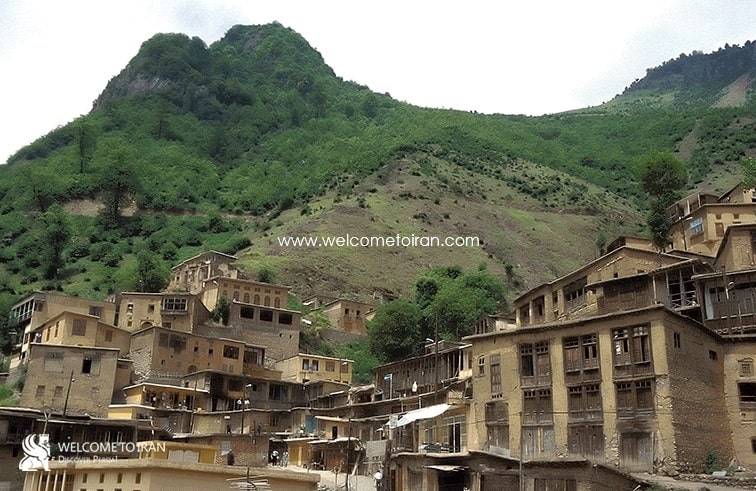

In the 10 km above the new village remains the old village with artifacts and human such as stone oven … that have been scattered in the area range which can be counted among the arte facts . Archaeological excavations conducted have been found the old pottery village belonging to the fifth to eighth centuries AD that they are accurate remarkable historical documentation. From 1385 Masouleh old village was in the national index.

The geography of the Masuleh village
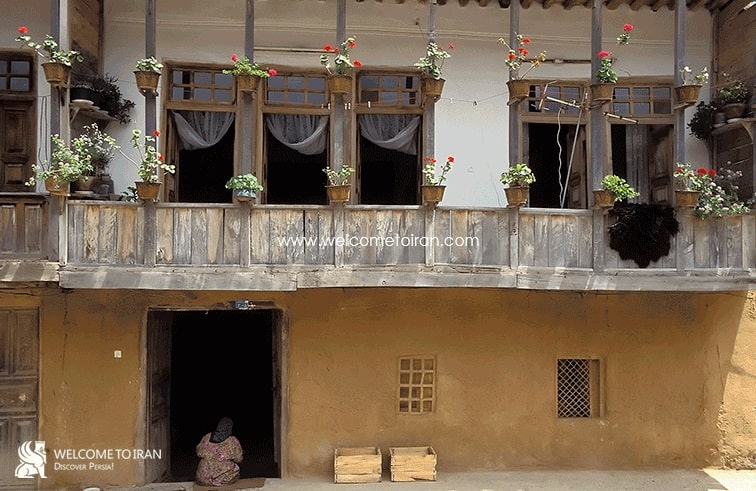
Today Masouleh city is a small village consist of traditional architecture that is with 100 hectares Green mountains located in the deep heart of nature is in the geographical coordinates 48 degrees, 59 minutes east longitude, and 37 degrees, nine minutes north latitude and the range of it from the north of the city to Masal, from the south to the Olia Tarom and from the East to the Fuman plain and from the west to the Khalkhal province ( Zanjan province), central area of village overlooks from three directions North, South and West to the mountain and from the East to the beautiful valley its height from the Free sea is 1050 meters with Mountainous climate with cool summers and cold and snowy winters. Surrounding of Masouleh covered by forests and the main connectivity road is a prolate way to the Fuman. Masouleh has a unique architecture. Driveway enclosure and roofs both use as the sidewalk. The village architectural fabric is formed during the Zandieh and small streets and many stairs do not let anyone to use the motor vehicle. Masouleh architecture is described in one sentence: Top buildings courtyard are roofs of the low buildings. Numbers of floors of buildings are usually 2.
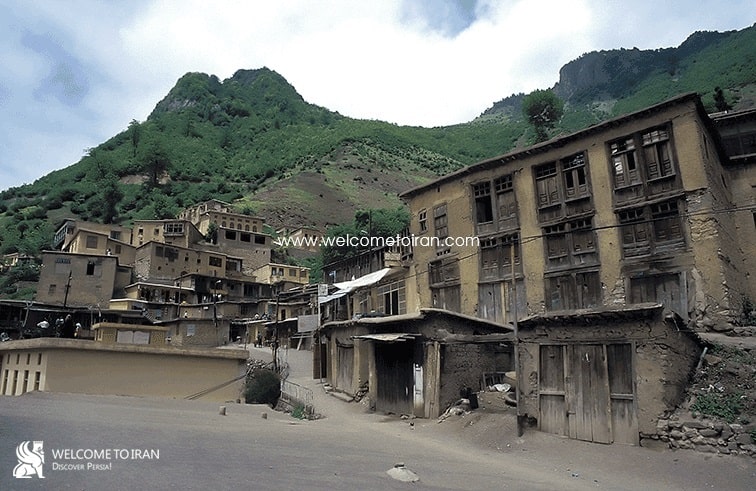

Neighborhoods villages of Masouleh
Masouleh Has a bazaar with 4 floors and 4 main parts:
- Khane bar (Khuna var)
- Masjid bar (Maza var)
- Key Sar ( contains: Kafa Key sar and Ben Key sar)
- Asade Mahale ( Asamal)
All of them in the independent mood have immediately associated with town Bazar. Now in Masouleh there are more than 350 residential units that are in the past (100 years ago), the number of units was 600. There is more than 120 commercial units within its market, More than 4 caravansarais, 2 Treasure bathrooms, More than 33 public fountains ( Khuni), 10 Mosque and 5 Shrines indicative of prosperity the city in recent periods. Masouleh population has declined over the past 60 years.
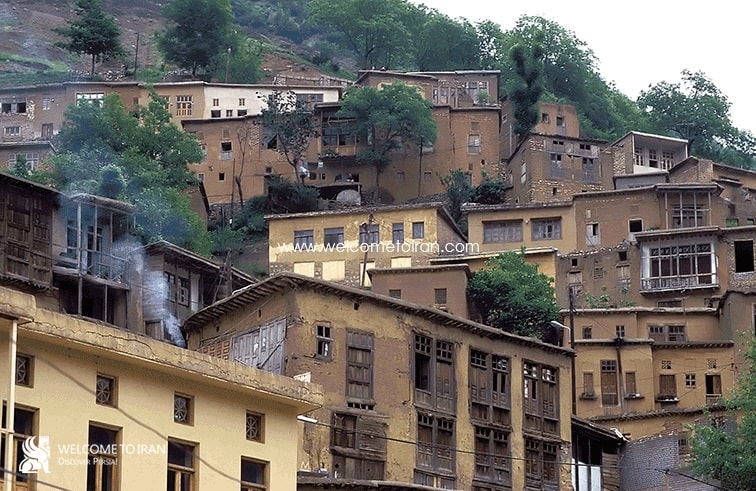

Economy of Masuleh
Being on the former communications highway and existence of eight caravansaries indicates this content that many peoples in Masouleh have been traded. Masouleh handicrafts contain : Wood and metal industries was common until about the sixties which is now completely destroyed . Now the village economy is based on tourism.
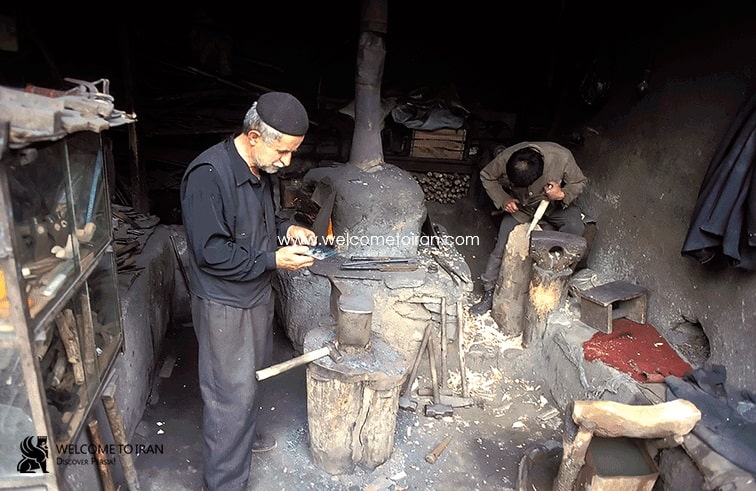

Genesis of Masuleh
The old Masouleh which is located in the “eight kilometers West Road of Khalkhal” was the original and primary settlement of the persons from Masouleh that now a day remain a stone wall building from that time. In the first archaeological excavations of the Fuman city that took place in September 1374 by the Archaeology Institute of Gilan Cultural Heritage, it was found that from fifth to eighth centuries this old village was one of the most important centers ijn the field of Metalworking . Also, Glazed pottery with various colors that have the characteristics of Seljuk time was discovered in this area this district because of its historical importance and validity was recorded in the national index in September 1385. About Masouleh persons moved to the current location there are many different opinions that one of the most important of that is one of the grandchildren of the first imam of Shias with one of the children of the seventh Shiite imam Musa al-Kazim whose his tomb is located in Astaneh Ashrafieh in Gilan was wounded in a battle near Tarom of Zanjan city and took the Masouleh village way and died in the current location of Masouleh and w as buried there .
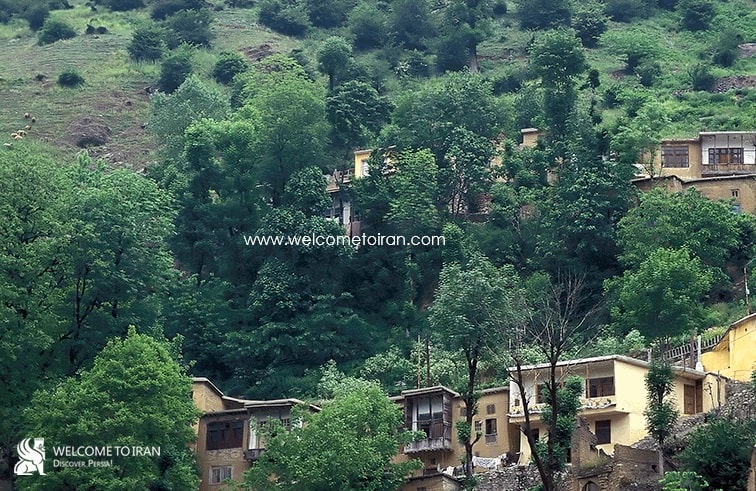

After that gradually the people from Masouleh were built their houses around his tomb and thus the current Masouleh was formed. One traditionary says the reason of Masouleh persons migration to the current location was due to great earthquake of 890 AD and also another traditionary mentioned the epidemics of plague in the year 943 AH in Iran as the reason of displacement. But later generations, not immanent in the new location and this city that was the trading center and highway between Azerbaijan and Gilan and Zanjan and Bazaars, caravanserais and metal and nonmetal industry and was boomed in these ways had a dramatic decline. In a part of time Masouleh was the center of gravity of the Gilan , Zanjan and-and Azerbaijan and it was one of the special importance of this village but with the creation of the main ways between Gilan and Azerbaijan, Gilan, and Zanjan from the other routes, Masouleh lost its economic boom and , followed by, its population occupation of the country during World War II in the year 1320 and the chaos from it , was effected on a Masouleh native people immigration . Masouleh municipal was founded in 1311 AH but it was closed in 1318 and it began to work again in 1341 AH. Masouleh persons have a great role in the history of the Forest movement against the invasion of Russia and Great Britain. Masouleh persons helped force Forest and someone like martyr Babaghlamly fought alongside them.

Masuleh language
The Original language of Masouleh persons as same as the people in West of Gilan and South of Azerbaijan Republic is “Talysh language” . Talysh language is one of the north-western Iranian languages and it is also for the person who speaks in this way. Talysh language is from the family of Caspian languages and it is very close to Tati language. “Talesh language” is also cognate with the other languages of Caspian Bank like “Gilaki” and “Mazandarani” but it has significant differences with them. Tat’s , Taleshy’s and Mazandarani’s peoples speak different languages that they are different from Persian language and similar to the Medo-Persian and Avesta languages. Talysh language is similar to Avesta and Kurdish languages. This language is close to the Azerbaijani ancient language. Talysh language is contained as a northwest of the Iranian languages that is very similar to Medo-Persian , Azeri, Avesta, old Azeri languages.

Origins of Masuleh people
Being Masouleh in the communication highway of Gilan and Azerbaijan and also having 8 Caravansaries confirms the fact that many old people have been commuting in this town and many people have been residing in the village over the years due to immigration and marriage. So you cannot say that the Masouleh persons are originally from Talesh and from the past as their language is similar to the Mare- Perthian they could easily have verbal communication with various Iranian tribes base on the language that they speak and also similarities to Avesta and Kurdish languages. Also, this language is close to the ancient Azerbaijani language. “Talysh language” is considered as Iranian Northwest languages and also it has lots of similarities with old Azeri language. Although Taleshi and Gilaki (the main language of center and East of Gilan ) are different from each other but from the past Masouleh persons speak Gilaki easily together due to associated with Fuman and also because of the multitude of relationship with Azerbaijan , most merchants were familiar with the Turkish language. Maybe you can define Masouleh persons as Non-agricultural people, and often have industry and trade, Iran consists of different ethnicities who knew Talysh language and they lived several generations together in the current location of the Masouleh And also due to speak a certain kind of Talysh language, on behalf of the people of the towns and nearby villages this village refers Masouleh.

Masuleh village culture
There is another significant point in the culture of Masouleh people, and this is that they are hospitable. What is left from the-the last rituals of Masouleh, is the Muharram traditional ceremony that it is the cultural-touristic attraction of Masouleh.
And it attracts huge crowds annually and the interesting thing is that, unlike many places, preacher and miracle play eulogies and actors do not get any money. As possible constructions in Masouleh is limited (only failure reconstructed) inhabitants and is fixed people that they are living there is lower than 1000 persons but dozens of Masouleh residents are still living in major cities of Iran and outside Iran. Masouleh Restaurant in Chicago, in the United States of America, represents the Masouleh village and Iranian and Gilani foods with the great managements of Mr. Nasiri Masouleh.

The appellation of Masuleh name
Masouleh name or with the original pronounce Masouleh in the Taleshi language from the ninth to the eighth century and later on used it in its current form. Someone said its came from the name of a mountain near the Masouleh village with the name of “Mahsalar”. They believe that this area was called “Masalar” at first and because of the plurality of application its transformed to Masouleh.

In another narrative, the word Masouleh is formed from the combination of two words : “Moss” and “Ole”. The first part of the Iranian culture means mountain and barrier and the second part is also meant high which in a combination with a diminutive “in” has come with the meaning of “like”. So “Masouleh” can have the meaning of “high mountain” or “Mount as”. Whit relying on Sanskrit and Persian Pahlavi it has also the meaning of the “little moon” or “land of the tiny moon”. Someone know this name derived from the name of “Mosul” in the Kurdish city and believe that the primary persons of Masouleh were Kurdish and had Izadi religion. Now if we pass from the history of Masouleh Muharram especial events and funeral in this Wadi there has not been paying attention to a simple difference between different kinds of “s” and also the similarity of the name of Masouleh and Masal (the city near the Masouleh) so it seems superficial interpretation this interpretation also makes other stories by biased or uneducated people that they had related Yazidis to the Yazid Umayyad Caliph…in another word Masouleh is the Arabic and Compound word from the words : “Ma”, “soo” ,“leh” with the meaning of “The place where poverty and ugliness don’t have any place”. Many researchers don’t know such justified and traditions properly. What seems more correct is due to the similarity of the name of the Masouleh and Masal , (A city near the Masouleh) and the village with the name of Khani Masouleh in the Masal city and also since at the beginning this name was related to the Old Masouleh(Talesh language Khan Masouleh) the main core of the Masouleh persons that have been moved to 8 KM lower from the Old Masouleh. Depending on the weather , land slope, it made for easier defended against marauding bands and also for adroit chain and as well as evidence such as Masouleh veterans dialect that even back to the Persian before the Arabs arrival. Masoulehis the city with very unsaid and unknown parts.

Masuleh registered in The World Heritage List
Masouleh global record from was put on the agenda from the year 90, but the lack of an integrated urban management and there were 11 Electrical Department , Water and Wastewater buildings,Telecommunications, meteorology, cooperative handicraft, health center, business unit, two residential units is a barrier in the green airspace over the global village .
To fix this problem in the first stage proposed that two office buildings of electricity and telecommunications temporarily transmitted for 3 to 5 years into the Masouleh tissue. That with the demolition of these two buildings the free part of green Masouleh airspace and the registration process will continue.

However, from the year 76 downstream areas of the historic fabric of the Masouleh was in the green airspace and construction was forbidden, but the problem of 11 heterogeneous buildings which are located in this part of the historical city has not been resolved yet.
Now device management server at a Masouleh historic city is separate. That based on the UNESCO condition should be integrated management. Masouleh historical city in 30.5.1354 was known as the first living historical city of our country and has been registered as a complete set in the national index Iran.
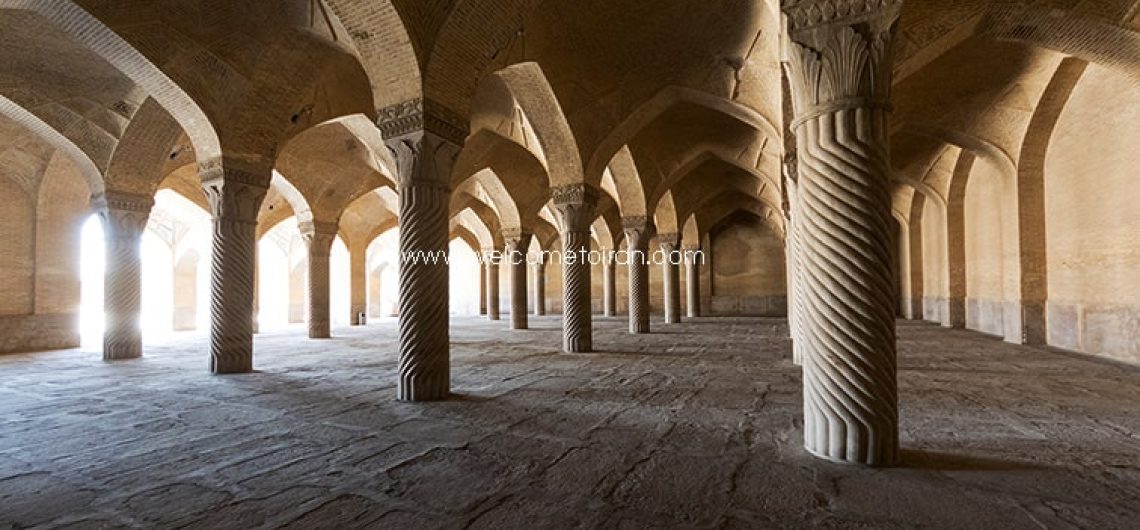
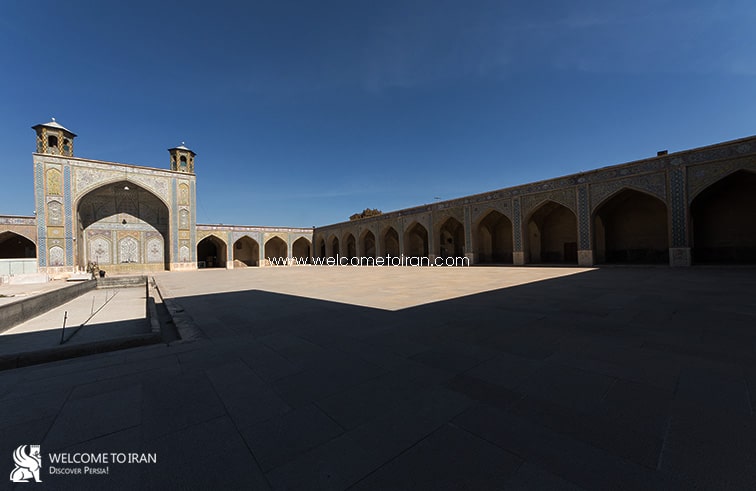
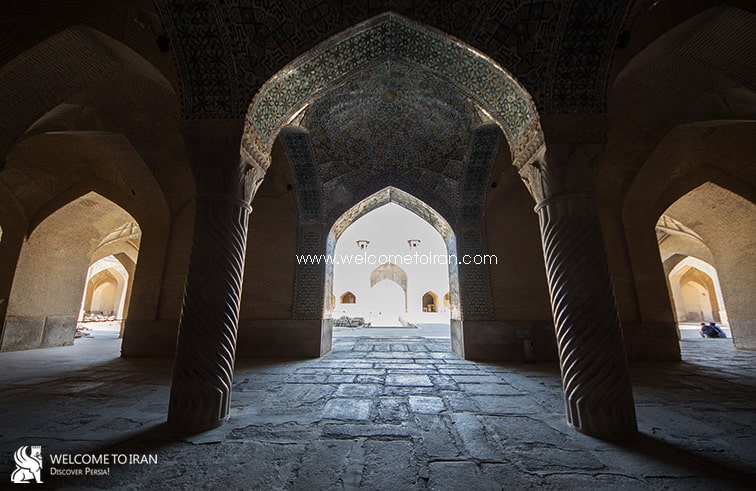











 Entrance
Entrance






















